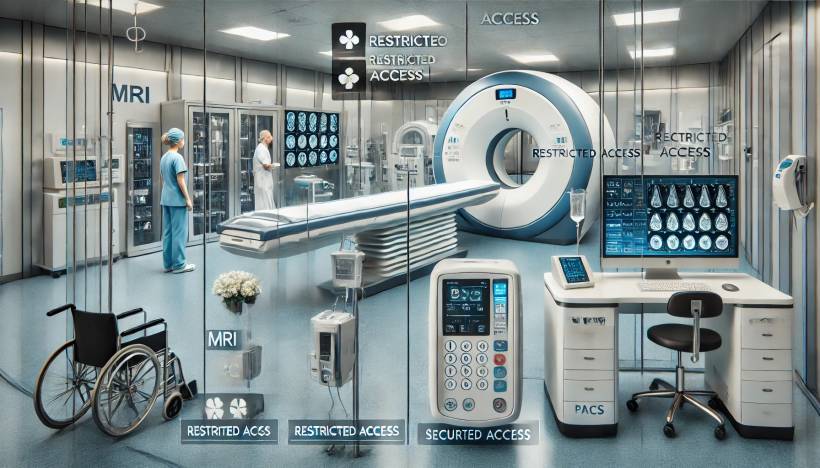
In the world of healthcare, security isn't just about protecting data—it's about ensuring patient safety. While cybersecurity gets a lot of attention, physical access control is just as crucial, especially when dealing with life-saving medical devices like MRI machines, CT scanners, infusion pumps, and PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems). So, how do hospitals and clinics prevent unauthorized access to these devices? Let's break it down.
1. MRI Machines: Keeping the Magnet Under Control
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines are incredible diagnostic tools, but they come with a catch—an extremely powerful magnet that never turns off. This means access control is vital to prevent accidents (imagine someone walking in with a metal chair—yikes!). Here's how access is managed:
- Zoning System: MRI areas are divided into four zones (I to IV). Only trained personnel can enter Zones III and IV, where the machine is located.
- Keycard or Biometric Entry: Doors leading to restricted zones require authorized access.
- Screening Protocols: Patients and staff are screened for metal objects before entering.
- Signage and Training: Clear warning signs and ongoing staff education help prevent accidental or unauthorized access.
2. CT Scanners: Shielding from Radiation Exposure
CT (Computed Tomography) scanners use X-rays, meaning radiation exposure must be carefully controlled. Unlike MRI machines, CT scanners don't have a permanent magnetic field, but physical access is still tightly regulated:
- Restricted Access to Radiation Rooms: Only radiology staff, trained technicians, and authorized personnel can enter.
- Lead-Lined Rooms & Shielded Doors: These prevent radiation leakage while limiting access.
- Interlocking Doors: Some facilities have automatic locking doors that prevent entry when scans are in progress.
- Surveillance Cameras: Monitored areas ensure that only the right people enter.
3. Infusion Pumps: Preventing Tampering & Unauthorized Use
Infusion pumps are used to deliver medication and fluids to patients accurately. Because incorrect dosages can be life-threatening, controlling who can access and adjust these devices is critical:
- Locked Pump Casings: Some pumps are enclosed in locked compartments, requiring a key or access code.
- Staff Authentication: Nurses and doctors must enter a PIN or scan a badge before adjusting settings.
- Tamper-Resistant Alarms: Any unauthorized attempts to open or modify the pump trigger alerts.
- Bedside Location Restrictions: In some settings, pumps are kept within patient care areas where only medical staff can access them.
4. PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems): Protecting Digital Access to Medical Images
PACS systems store and transmit sensitive medical images (X-rays, MRIs, CT scans). While this is more about digital security, physical access to workstations and servers is still critical:
- Restricted Server Rooms: PACS servers are kept in secure data centers, requiring keycard or biometric access.
- Workstation Access Controls: Only authorized personnel can log into PACS terminals.
- Privacy Screens: Monitors in public areas may have privacy screens to prevent unauthorized viewing.
- Automatic Logouts: Systems automatically log out inactive users to prevent unauthorized access.
Final Thoughts
Physical security in healthcare isn't just about locked doors—it's about patient safety. Whether it's preventing accidents in MRI rooms, limiting radiation exposure in CT scan areas, safeguarding infusion pumps from tampering, or protecting medical images in PACS, hospitals implement multiple layers of security to ensure that only the right people have access.
So next time you visit a hospital, take a moment to notice the security measures in place. They might not be obvious, but they're working behind the scenes to keep both patients and medical professionals safe!




Comments