As off year 2014, we have seen vast improvement over the utilisation of Information Technology (IT) throughout Malaysian's industries. Harmonized with a vision that was established way back during year 1996, we are progressively on track in achieving Vision 2020's Multimedia Super Corridor (MSC) and thus achieved strategic competitive advantages in economy based on knowledge. Online Wikipedia states that Economy based on knowledge or widely known as K-Economy (Knowledge Economy) is the use of knowledge to generate tangible and intangible values to help transform a part of human knowledge to. This knowledge can be used by decision support systems in various fields and generate economic values which will be beneficial to Malaysian industries.
1. INTRODUCTION
Our economy is in transition towards K-Economy, whereas it is an extension of an information society in the information age led by innovation, such as providing the development platform for engineering physics, the use of robotic artificial intelligences (AI) in manufacturing and more. This transition requires that the rules and practices that determines the success in the economy in need of rewriting in an interconnected, globalised economy where knowledge resources such as know-how and expertise are as critical as other economic resources.As we journey on to this new information era where it is continuingly progress with its rapid pace of IT development and computerised systems being heavily used in almost all types of industries such as educations, banking, manufacturing sectors, transportations and many more, the demand by these fields has increased in line with development of many types of complex systems to cater such economic demands.
So, where are we now in utilisation of IT and computing in today's modern world? As mentioned before, vast improvement has been seen throughout most of the major industries in Malaysia as we can see the demand for IT is rapidly growing each year. As we remembered back in the year 2000, if we flip through newspaper looking for job sections, we can't hardly see any job demands for IT based jobs. But in today's world, when we flipped over newspaper, we can see high demands for IT based jobs such as Database administrators, System administrators, Programmers, and even a basic clerical job nowadays requires basic IT knowledge such as the capabilities to use simple word processing computer applications such as Microsoft Words and Excel.
Therefore, IT is being aggressively utilised in almost all industry sectors such as education, banking, transportations and telecommunications and more.
2. EDUCATION SECTOR
IT in education sector is one of the most important tool for Malaysian's learning institutes. This can be seen as utilisation of IT and computing are rapidly growing year by year. This growth would definitely improve learning process and at the same time providing better facilities to facilitate the learning environment for the students.2.1 - Education Facilities
So let us look into how IT being applied in education facilities nowadays. With the aggressive movement in Information Technology sector, more and more computer applications are being developed in effort to provide a broader choice of learning facility available.
Digital Library
One of the major and most important facility is a library, which contains books, journals, research articles and others. With IT being applied to this facilities, some learning institutes such as Open University Malaysia (OUM) has developed a pure online digital library storing digital books, journals, articles as students can easily retrieve the required information without to physically visits to the library to check out on a book.
According to E.A. Fox, the digital library may be defined as the "New way of carrying out the functions of libraries encompassing new types of information resources, new Approaches to classification and cataloging, intensive use of electronic systems and networks and dramatic shifts in intellectual, organizational and electronic practices". (E.A Fox, 2003)
With Digital Library being applied, students can easily retrieve their book online, and at the same time students can easily search for the required information with the unique web-based applications that allows users to search by keywords or specific terms to enhance their search queries when searching for the required books, articles or journals.
Electronic Learning (E-Learning)
Back in the old days, learning process is limited as it is being only facilitates in a conventional class rooms. However, with IT being applied to education sector, we can see that most universities nowadays are trying to broaden their learning spectrum for students by providing more alternate ways in learning. Students will have varieties of learning tools such as online learning modules featuring videos of lectures on the learning subject, rich multimedia contents to help aid students to visually understand better of the subjects and more instead of heavily relying on attending class and reading books.
Some of the E-Learning examples are as per following:
| Learning modules in text format for reading materials |
| Online lecture, featuring video of the lectures on the learning subject |
| Discussion forum where students can discuss among other students |
| Online Frequently asked questions (FAQ) and answers by students |
| File repository of past exams questions, useful documents prior to the learning subjects |
| And many more |
Administrative Improvement in Education Institutes
Let's talk about how IT being utilised in education administrations in Malaysia. Few years back, when we want to apply for enrollment to any Malaysian universities, we had to physical retrieve the required form, fill up the form with the required information and submit it to them. However, nowadays most universities encourage students to submit their application for enrollment via online.It's not only limited to enrollment process, but to other administrative tasks. Below is the list of how IT helps education institutes in administrative tasks:
| Online enrollment process where students can submit their applications online instead of submitting hard copy of the application forms to the universities administrations. |
| Student management done via computer nowadays instead of hard copy paper. For example, student profile is saved in database instead of file cabinet. This makes searching for information a lot faster when using computer. This also applies to other documentations such as exam results, academic performance and more. |
| Collaboration between other learning institutes nowadays are easy. For example, Malaysian Qualifications Agency (MQA) which collaborates learning institutes within Malaysia for student's academic purposes such as results, defining a standards in an education and more. |
| And many more |
With IT being utilised in administrations, learning institutes can gain enormous advantages in providing a quality education to the students, thus increase the level of education rendered by our local universities.
2.2 - Challenges and Issues in Education Sector
While IT is aggressively growing in education sectors, there are some challenges and issues as well. There are few local universities are still applying conventional study methods as some students prefers traditional ways in learning. With the aggressive movement in IT, more and more computer applications are being developed in effort to provide a broader choice of learning facility available. It would be a huge loss for both learning institutes and students if they are not aware of this or did not fully utilize the tools provided to aid them in their studies.Government should invest more in creating awareness on the importance of IT in education sectors, but not only limited to students but to learning institutions as well. These awareness programs helps open the eyes for those who are still living in the previous era as we need to make them realize that we are moving forward towards an information era. At the same time, the benefits of utilising IT in education sectors helps to reduce costs in terms of money, manpower, and time as well.
Aside from these issues, shifting towards a new technology will always requires an ample amount of investment as learning institute's management might need to consider trainings, IT facilities and more as these facilities are quite expensive.
3. TELECOMMUNICATION SECTOR
The telecommunications industry in Malaysia experienced a significant growth over the years ever since the MSC bill was introduced in 1996. Referring to the Commission reports, the total number of mobile subscriber increased from 2.7 million at the end of 1999 to 7.5 million at the end of 2001 while mobile penetration increased from 12.0 percent to 31.4 percent during the same period. The following table sets out certain information relating to the telecommunications industry in Malaysia as at 31 December 1999, 2000 and 2001.That was back in year 2002 showing telecommunication growth when the MSC bills was introduced. Today, our mobile penetration in Malaysia is at 140% as everyone is having mobile phones and some may have multiple mobile phones at their disposal.
Now let's discuss the era of mobile smartphones. A recent article from the The Star newspaper states that in 2013 the mobile smartphone penetration has increased to 63 percent from 47 percent from the previous year. The study is based on an online survey which queried 500 urban users who use the Internet daily, and are aged between 16 and 60. With the statistic above, we can conclude that from year 2002 till 2013, the increment of smartphone penetration is at 31.6% while tear 2012 to 2013 shows the significant increase.With the rapid change in technology, telecommunication industry has been the most aggressive growing industry, not only to Malaysia but globally. Imagine yourself using a mobile phone bought five years ago, people will treat your phone as an obsolete device and incapable of copping with any new technologies that are currently in trend.
3.1 – Mobile Phone Evolution
Telecommunications has evolved over the years. Remember back in the old days where mobile phone is only being used for calls and short messages? With today's technology, phone is not only limited to calls and messages but offers more features such as online browsing, viewing multimedia contents, personal organisers and more.
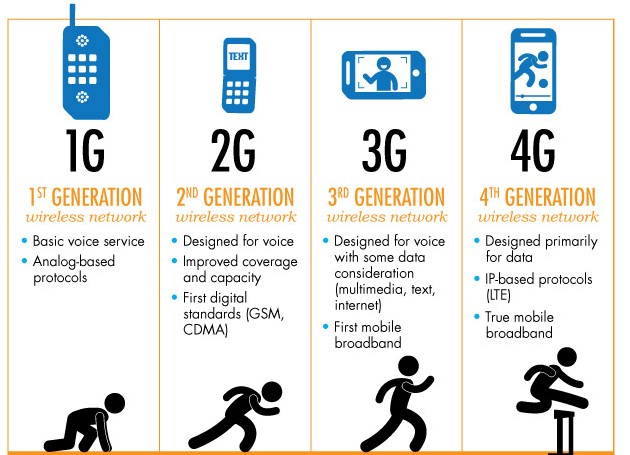
Based on figure 1 above, we can see that the phone technology has evolved over the years. Refer below for further details:
| 1st Generation: Analog-based technology that was used during 1979 – 1990. Mobile phone is only capable of making calls and receiving calls only. |
| 2nd Generation: The second generation of phone is capable of transmitting data wirelessly therefore providing users with messages (SMS) services. At the same time, mobile phone is also capable of browsing to internet at GPRS and EDGE speed during this period. This was being used during 90s and early 2000. |
| 3rd Generation: More commonly known as 3G and was initially introduced during the year 2001. However, Malaysian telecommunication industry only began to adept to this technology during the year 2006 and above. Highlight of this generations is the phone is capable of browsing the internet at a high speed which varies from 384 kilobits per seconds (UMTS / 3G technology) and up to 7.2 megabits per second (HSPDA / 3.5G technology). |
| 4th Generation: Latest communication technology which is widely known as LTE. Offering speed of about 10 times faster than the 3G technology. |
3.2 - Challenges and Issues in Telecommunication Sector
Telecommunication sectors are the most aggressive and competitive industries in Malaysia. Major telecommunication organisations such as Maxis, Celcom, and Digi are the top main players in providing this services while other new startup company struggles due to this aggressive competitive trend.
One of the most major drawbacks of the rapid change in mobile technologies is the amount of investment needed in order to cope with this rapidly fast growing industry. Imagine yourself that you've had to change your phone frequently at a minimum of 2 years once, and while you have to still bear the cost of your phone usage which is paid to your telecommunication service provider. Now let's look this from the business perspective instead of personal. Imagine yourself as a telecommunications service provider, and new technology is out on the market which is 4G LTE. Imagine the amount of cost needed to upgrade your existing facilities in order to provide up to date technologies to your end users. This does not includes the costs of trainings, installation and more.
4. TRANSPORTATION SECTOR
The transportation sector is one of the most important component in Malaysian economy which affects the development and the welfare of Malaysian people. A good and efficient transportation system is a prerequisite for the economic development of Malaysia, and utilisation of IT in this industry will definitely improve the development and growth of transportation industry in Malaysia.
4.1 – Energy Efficiency Technology
Transportation sector has been regarded as the second most energy consuming sector accounting for about 40% of total energy consumption in Malaysia. The transportation sector is one of the most energy intensive sectors in the country and heavily relies on petroleum-based energy. When comparing with other countries, Malaysia experienced a high level of motorization since 1990. Total numbers of road users are much higher compared to other nations. Therefore, transportation system energy issues will need to be addressed.
In lieu with this issues, with the utilisation of IT in transportation helps transportation sector in creating a more energy-efficient vehicles for the automotive industries. As we can see today, more and more buyers are becomingly aware of this issues as they seeks for a more energy efficient vehicle in effort to reduce fuel consumption.
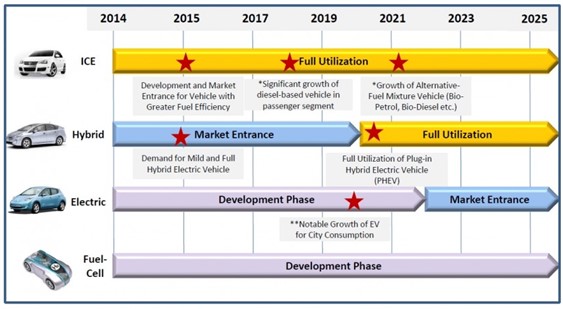
This year, Malaysian Automotive Institute (MAI) together with Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI) has introduced new objectives and milestones for our current National Automotive Policy (NAP) for the year 2014 and one of the key objectives for NAP 2014 was to develop Malaysia as the regional automotive hub in Energy Efficient Vehicle (EEV).
Referring to figure 2, it shows the roadmap for the development phases and market penetration for the mentioned NAP 2014 objectives. With NAP 2014 being implemented, automotive manufacturer will more and more relies on IT in their business process, manufacturing processes and technological advancement in effort to achieve an energy efficient vehicles.
4.2 – Technology Advancement in Malaysian's Public Transport
Let us look in what has changed since 1990. Back in the old days, Malaysian people relies on public busses and trains in order to commute from one point to another destination. They wasn't many options to public transportation as we can either take the bus, train or taxi.
Now as we are approaching to year 2020, Malaysian public transportation has vastly improved and offering Malaysian with multiple choice of public transportation. Let us look into what we have now:
| KTM Komuter was the first electric train in Malaysia. |
| KLIA Express train is a high speed train travelling at a maximum speed of 160 km/h. Also known as bullet train. |
| KL Monorail is a unique train that travels on a single dual-way line that connects certain part of Kuala Lumpur. Previously it was owned by KL Infra Group which was declared bankrupt back in 2007. However, currently it is owned by Rapid Rail Sdn Bhd. |
| Light Rail Transit (LRT). Previously known as Star LRT and Putra LRT, however as off 2012 Rapid Rail Sdn Bhd had owned all these transit system. |
4.3 – Challenges and Issues in Transportation Sector
Biggest challenge or issues with IT development in transportation is the high business risks and high costs involved in innovation and renovation of any transport technology. As we can see, few major corporation had declared bankruptcy due to the high costs of the development and at the same time the return on investment (ROI) are at a very low level.
5. BANKING SECTOR
Moving towards to the new information era age where it is an age of computing, communications, information and knowledge, banking industry has been revolutionised from paper and branch banks to an era of digitized and networked banking services. This affects and changes from internal accounting and management systems of banks and at the same time changes the delivery systems of banks. It is clear that with the rapidly changes in IT, banking industry struggles to find a technological solution to meet this challenges. Banks with the ability to invest and integrate IT to its business will have a competitive advantages over other banks, therefore investment in IT is critical especially to banking industries. Its potential and consequences on the banking industry future is enormous.
5.1 – Improvement for Bank Customers
Today, bank customers will find themselves a lot of options and facilities provided by the banks to help assists them in their daily banking tasks. With more and more sophisticated IT applications being developed, customer nowadays can enjoy many new IT based facilities for their banking activities. These includes the following:
| Better inquiring facilities are now available which make the bank easier to check on the credit liability of a person's when the customer is applying for a loan. For example, banks are now using CCRIS and CTOS applications to check on the credit report for a customer which will aid the banks in defining the liability level of processing the loans. |
| The use of computer applications that aids the banks in generating a periodical reports on the returns of investments (ROI) such as MIS reports and more. |
| With IT in communications improved, banks will have a faster and up-to-date information transfer which enables banks to provide speedier decisions by interconnecting branches, controlling offices and even banking associations such as MEPS, KWSP. For example, loan application approval nowadays can be as fast as 30 minutes since decisions can be made speedily with the improved communications facilities. |
| And many more |
5.3 – Challenges and Issues in Banking Industry
While banking industry in Malaysia began to fully utilise the use of IT in their operations, it can also leads to some potential dangers and issues to be taken into account. With the introduction of E-Banking facilities, the most major threats to banking industries nowadays will always be cyber terrorism as bank industries need to invest high amount of money for their cyber security. Cyber terrorism act such as phishing, database sql injections, web hacks are a common terms as bankers need to be pro-active in countering the cyber threats.
5.4 – Challenges and Issues in Banking Sectors
While IT is aggressively growing in education sectors, there are some challenges and issues as well. There are few local universities are still applying conventional study methods as some students prefers traditional ways in learning. With the aggressive movement in IT, more and more computer applications are being developed in effort to provide a broader choice of learning facility available. It would be a huge loss for both learning institutes and students if they are not aware of this or did not fully utilize the tools provided to aid them in their studies.
6. CONCLUSION
The 21st century will bring about an all embracing convergence of computing, communications, information and knowledge. There is no doubt that IT will change the way we live, work and think. The growth of IT utilisation in most major industries in Malaysia will definitely be a great transition towards the new age of information era.
However, there are few serious challenges and issues needed to be address first in each sectors as discussed earlier. While industries began to adapt to the new IT technology, at the same time it will also open up to a new possibilities of threats, challenges, and issues. Therefore, it is at a great importance that a research and survey to be carried out first before shifting towards to the new IT technology. Nevertheless, technology alone will not only create advantages but provides uncertainty risks to the business.
Hence before adapting to the new technological changes, it is vital for an organisation to conduct a research on how it will impacts the business, and studies on any foreseeable threats, issues and challenges that may occurs in the future. While this effort would much definitely consumes time and money, keep in mind that it is a great investment in doing so to avoid any uncertainty risks in the future.
Wikipedia - Knowledge Economy (2014), www.wikipedia.com [Online]
Rerences
E.A Fox, O Sornil (2003), Digital Libraries, John Wiley and Sons Ltd
Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commision, (MCMC)'s Statistics (2002). (formerly known as Malaysia Commision)
The Star Online (2013), Smartphone penetration hits 63% in Malaysia, www.thestar.com.my/tech/tech-news/2013/09/12/smartphone-and-tablet-penetration-hits-63-percent.aspx [Online]
Phone Arena website (2014), 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G: The evolution of wireless generations. www.phonearena.com/news/1G-2G-3G-4G-The-evolution-of-wireless-generations_id46952 [Online]
Malaysian Automotive Insurance (MAI) analysis (2014), Malaysia Automotive Technology Projection 2013 – 2025.
Wikipedia - Rail Transport in Malaysia (2014), www.wikipedia.com [Online]
Few years back, i was given an assignment paper for my studies on Basic Concepts of Information Technology. The assignment paper was about an in-depth discussion about Information Technology Utilisation in Malaysia. I have decided to publish my written articles here after one year from the assignment date. This is due to avoid any plagiarism issues that i might encountered if i publish this earlier than that.
You may download the published assignment paper here.